Did you know that nearly half of all online searches are now conducted via voice? With the proliferation of smart speakers and virtual assistants, voice search isn’t just the future—it’s the present. Due to this shift, businesses must reevaluate their SEO strategies, especially small and medium businesses (SMBs) in Canada and the U.S.
Advanced AI models like OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and Perplexity AI are transforming search algorithms and changing how users interact with technology by making conversations more natural and precise.
This blog will explore what voice search and Large Language Models (LLMs) mean for your business. We will explain how these technologies are reshaping user behaviour, outline the key differences between traditional text-based search and AI-powered voice search, and provide actionable SEO strategies to help you stay ahead of the curve in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Table of Contents
- Key Differences Between Traditional Search and AI-Powered Voice Search
- Voice Search and the Role of Large Language Models
- SEO Strategies for Optimizing Voice Search in the Age of ChatGPT and LLMs
- Metrics for Measuring Success in Voice Search SEO
- Ethical and Privacy Considerations in Voice Search SEO
- The Future of Voice Search and SEO in the Age of LLMs
- Conclusion
Key Differences Between Traditional Search and AI-Powered Voice Search
As Large Language Models (LLMs) continue to reshape the search landscape, it’s crucial to understand how voice search differs from traditional text-based search. These differences impact how users interact with search engines and how businesses should approach their SEO strategies.
Let’s examine the key distinctions:
| Characteristic | Text Search | Voice Search |
| Query Length | Short, keyword-heavy | Longer, conversational |
| Example Query | “best HVAC services Toronto” | “What’s the best HVAC service near me that offers 24/7 support?” |
| Language Processing | Basic keyword matching | Advanced Natural Language Understanding (NLU) |
| Context Understanding | Limited | Comprehensive analysis of query context |
| Result Display | List of website links | Zero-click results, featured snippets, direct answers |
| User Interaction | Single query | Supports multi-turn conversations |
| Optimization Focus | Keywords | Intent-based, conversational content |
| Local Search Importance | Moderate | High (many voice queries have local intent) |
| Content Structure | Less critical | Crucial (clear, concise answers for featured snippets) |
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
LLMs like GPT-4 excel at understanding natural, conversational language, meaning they’re better equipped to handle complex queries than traditional search algorithms. These models analyze the context behind each query to provide more precise answers, making intent-based search optimization crucial.
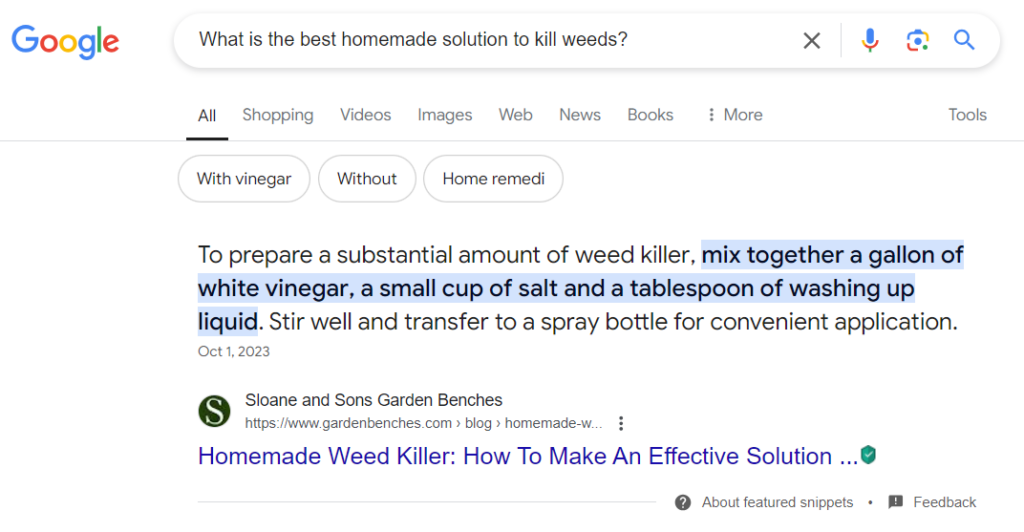
Zero-Click Results and Featured Snippets
As LLMs evolve, zero-click results—where answers are displayed directly at the top of search results or spoken by voice assistants—are becoming more important. For instance, if someone asks, “How can I get rid of weeds naturally?”, Google Assistant may read a featured snippet from a gardening website, and the user may never visit the actual page.
Optimizing for featured snippets and direct answers is vital. Structure your content to answer common questions clearly and concisely, increasing your chances of being the voice search result.
Conversational Search
LLMs support multi-turn conversations, allowing users to ask follow-up questions. For example, if a user asks, “What’s the best dentist in Vancouver?” and follows up with, “Do they offer Saturday appointments?”, LLMs can track the conversation and offer more personalized results.
Voice Search and the Role of Large Language Models
Voice search allows users to speak their queries instead of typing them, making interactions with technology more conversational and natural. This technology utilizes speech recognition to understand spoken words, enabling quick and hands-free access to information. Voice search has significantly evolved thanks to AI-driven voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Google Assistant.
As of 2024, voice assistant usage continues to rise:
- Global Usage: 30% of internet users aged 16 to 64 worldwide use voice assistants each week (DataReportal).
- U.S. Smart Speaker Ownership: Around 98 million Americans own a smart speaker in 2024 (Edison Research).
- Voice Query Users: Approximately 86.1 million U.S. smart speaker users askquestions via voice in 2024, up from 80.2 million in 2022 (eMarketer).
- Generational Usage in the U.S.: 61.9% of Millennials, 55.2% of Gen Z, and 51.9% of Gen X use voice assistants monthly on any device (eMarketer).
Voice search isn’t limited to smartphones and speakers anymore; it’s also integrated into cars, TVs, appliances, and even remote controls, expanding its reach and influence on daily life.
What’s fueling this change in search behaviour? The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs)—advanced AI systems that understand and generate human-like text. Models like OpenAI’s GPT-4 (ChatGPT), Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and Perplexity AI process and interpret the nuances of language, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of voice search results. They make interactions with technology feel more like a conversation with a real person.
How LLMs Power Voice Search
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): LLMs use advanced NLU techniques to grasp user intent, even when queries are vague or complex. This means they can understand slang, colloquialisms, and context-specific language nuances.
- Contextual Responses: With conversational abilities, LLMs can handle follow-up questions and offer more personalized, contextually relevant responses. With their conversational abilities, LLMs can handle follow-up questions and offer more personalized, contextually relevant responses. For example, after asking about the weather, a user might ask, “Do I need an umbrella today?” and the AI can provide an appropriate answer.
- Zero-Click Results: Instead of merely providing a list of websites, AI-powered voice assistants often give direct answers, reshaping SEO strategies and search results. This shift means that businesses need to optimize their content to be the featured snippet or the primary source of information for voice queries.
SEO Strategies for Optimizing Voice Search in the Age of ChatGPT and LLMs
Optimize for Conversational Keywords
Voice searches are typically longer and more conversational, so your content should reflect this natural language pattern. Focus on long-tail keywords and natural-sounding phrases.
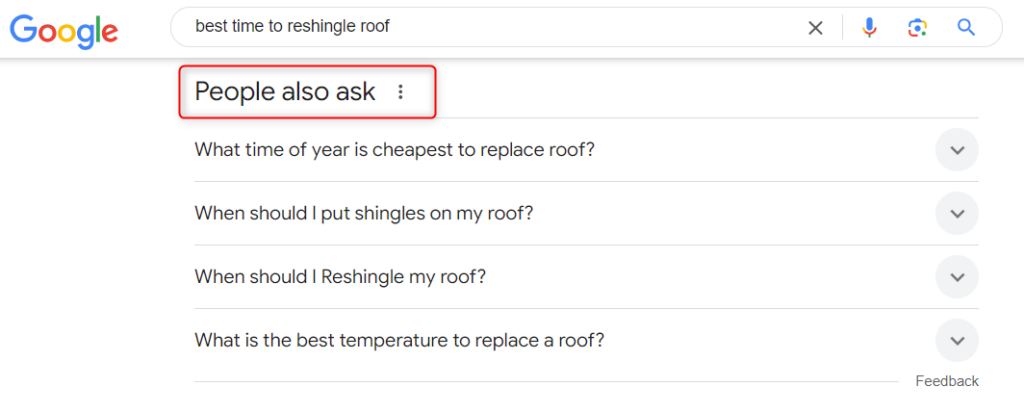
- Research conversational keywords using tools like AnswerThePublic, Google’s “People Also Ask” section, or by analyzing voice search data in Google Search Console.
- Incorporate these keywords naturally into your content, especially in headings, meta descriptions, and opening paragraphs.
- Example: Instead of targeting “landscaping company,” optimize for “best local landscaping company for small yards in [City Name].”
- Consider semantic search by including related topics and synonyms to cover the breadth of potential voice queries.
Using Structured Data and Schema Markup
Implementing schema.org markup helps voice assistants understand and feature your content more effectively.
- Use specific schema types relevant to voice search:
- LocalBusiness for location-based queries
- FAQPage for common questions
- HowTo for instructional content
Here’s an example of a schema markup for a local business:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "http://schema.org",
"@type": "LocalBusiness",
"name": "Your HVAC Company Name",
"url": "https://www.yourhvaccompany.com",
"address": {
"@type": "PostalAddress",
"streetAddress": "123 Main Street",
"addressLocality": "Toronto",
"addressRegion": "Ontario",
"postalCode": "M5A 2V6",
"country": "Canada"
},
"geo": {
"@type": "GeoCoordinates",
"latitude": 43.6532,
"longitude": -79.3832
},
"telephone": "+1 416 555 1234",
"email": "info@yourhvaccompany.com",
"openingHours": "Mo-Fr 09:00-17:00",
"image": "https://www.yourhvaccompany.com/images/logo.png",
"priceRange": "$$",
"description": "Your HVAC Company is a leading provider of heating and cooling solutions in Toronto."
}
</script>- Use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or plugins like Yoast SEO to implement schema markup more easily.
Optimize for Local SEO
Many voice searches have local intent, so local SEO is crucial.
- Optimize your Google Business Profile by keeping all information accurate and up to date, choosing relevant categories and attributes, and regularly posting updates and offers.
- Maintain NAP consistency (Name, Address, Phone) across all online platforms.
- Encourage and respond to reviews on Google and Yelp.
- Create location-specific landing pages for multi-location businesses.
- Build local backlinks through community involvement and local partnerships.
Target Featured Snippets
Voice assistants often pull answers from featured snippets. Structure your content to increase the chances of being featured:
- Use clear, concise language to answer common questions.
- Format content for different snippet types:
- Paragraph snippets: Provide a 40-60 word summary answering the main question.
- List snippets: Use bullet points or numbered lists for step-by-step guides.
- Table snippets: Present comparative information in table format.
- Use header tags (H2, H3) to structure content, with questions as headers.
- Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to identify featured snippet opportunities in your industry.
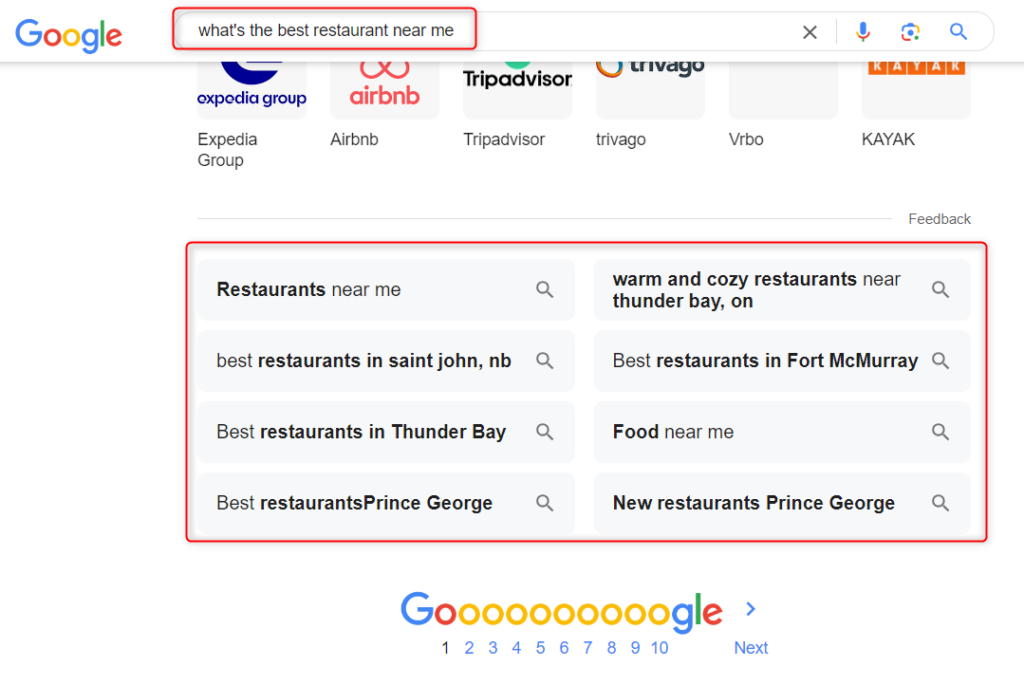
Focus on Question-Based Content
Voice queries are often phrased as questions. Tailor your content to address these directly.
- Identify common questions through customer service logs and FAQs, social media listening, and keyword research tools that focus on question-based queries.
- Create comprehensive FAQ pages, structuring each Q&A pair with proper heading tags.
- Use natural, conversational language in your answers.
- Provide concise answers (1-2 sentences) and more detailed explanations.
Optimize Page Speed and Mobile Responsiveness
Fast-loading, mobile-friendly pages are crucial for voice search success.
- Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights and Mobile-Friendly Test to assess your site.
- Implement speed optimizations:
- Compress images and use next-gen formats.
- Minimize CSS, JavaScript, and HTML.
- Leverage browser caching.
- Ensure your site design is responsive and works well on all device sizes.
Create Long-Form, In-Depth Content
Comprehensive content helps address various aspects of voice queries while establishing authority.
- Develop detailed guides and long-form articles (1,500+ words) on key topics in your industry.
- Structure content with clear headings and subheadings for easy navigation.
- Balance concise answers for voice queries with in-depth supporting information.
- Use internal linking to connect related content pieces.
Leverage Social Media and Online Mentions
Social signals and online mentions can influence voice search rankings.
- Maintain active, engaging social media profiles.
- Encourage user-generated content and social sharing.
- Seek opportunities for online mentions through:
- Guest posting on industry blogs.
- Participating in podcasts or webinars.
- Engaging in community forums or Q&A sites like Quora.
Metrics for Measuring Success in Voice Search SEO
Engagement Over Clicks
With zero-click results becoming more common, traditional metrics like click-through rates (CTR) are no longer sufficient. Focus on engagement metrics such as:
- Time on Page: This indicates how useful the content is after a user arrives
- Bounce Rate: High bounce rates could suggest your content isn’t delivering what voice searchers need.
- Conversions: Track whether voice search results are driving users to take desired actions, such as making a call or scheduling an appointment.
Voice Search Analytics Tools
Tracking voice search performance can be challenging, but tools like Google Search Console can help identify the voice-specific queries driving traffic to your site. Platforms like SEMrush or AnswerThePublic can offer insights into the most common questions your audience is asking, helping you optimize content for voice search.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations in Voice Search SEO
With the rise of voice search and AI-powered assistants, concerns around data privacy and ethical AI use have emerged. Voice searches often collect sensitive data, and businesses must be cautious about how that data is stored and processed.
As you optimize for voice search, consider implementing transparent privacy policies and ensuring compliance with data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
The Future of Voice Search and SEO in the Age of LLMs
As LLMs like GPT-4 (ChatGPT), and Google’s Gemini evolve, voice search will become even more intuitive and powerful. For SMBs in Canada and the U.S., success lies in adapting to this AI-driven landscape by focusing on contextual content, optimizing for featured snippets, and improving local SEO.
Future trends may include:
- Multimodal AI assistants capable of integrating text, voice, and visual searches seamlessly.
- Predictive voice search using AI to anticipate user needs before they even voice a query.
- Enhanced personalization through AI-powered voice assistants that understand individual preferences and past interactions.
By staying ahead of these trends and optimizing for voice-first search experiences, your SMB can ensure it’s part of the conversation and a leading voice in it.
Conclusion
Voice search, powered by LLMs like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and others, reshapes how consumers interact with businesses. For SMBs, this presents both challenges and opportunities. The key to staying competitive is adapting your SEO strategies to AI-powered voice search’s conversational, context-driven nature. Focus on local SEO, optimize for featured snippets, and leverage schema markup to ensure your business thrives in this evolving landscape.



